Signaling Pathways Leading to mTOR Activation Biology Diagrams
Signaling Pathways Leading to mTOR Activation Biology Diagrams The mTOR signaling pathway plays a central role in key processes, e.g., cell growth, metabolism, proliferation, and autophagy . Acting as a central regulatory factor and nutrient sensor, mTOR modulates cellular growth and metabolism by adjusting survival strategies and energy metabolism in response to changes in the external environment and
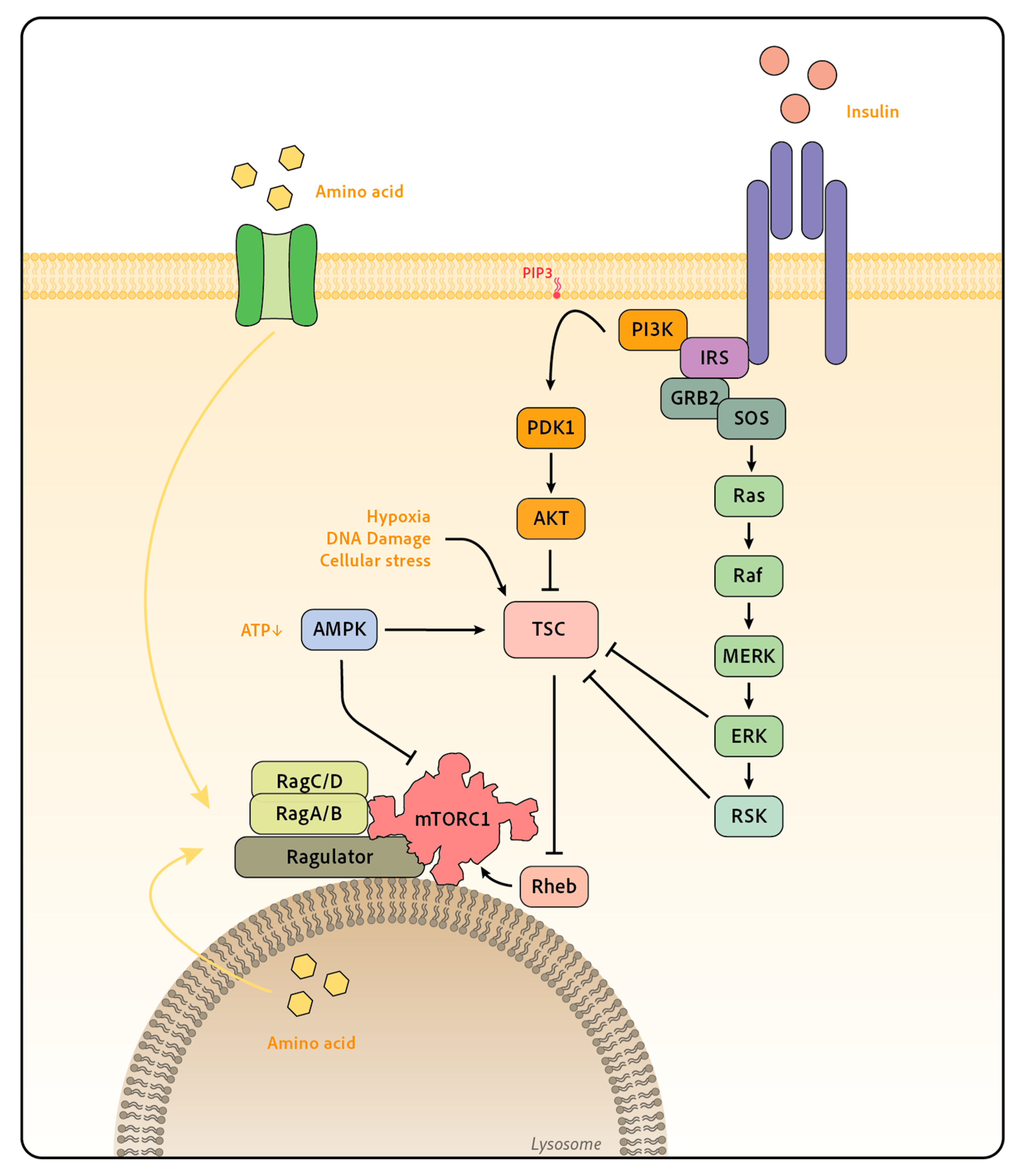
In all eukaryotes, the target of rapamycin (TOR) signalling pathway couples energy and nutrient abundance to the execution of cell growth and division, owing to the ability of TOR protein kinase

PDF mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease Biology Diagrams
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway senses and integrates a variety of environmental cues to regulate organismal growth and homeostasis. The pathway regulates many major cellular processes and is implicated in an increasing number of pathological conditions, including cancer, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and neurodegeneration. Here, we review recent advances in our
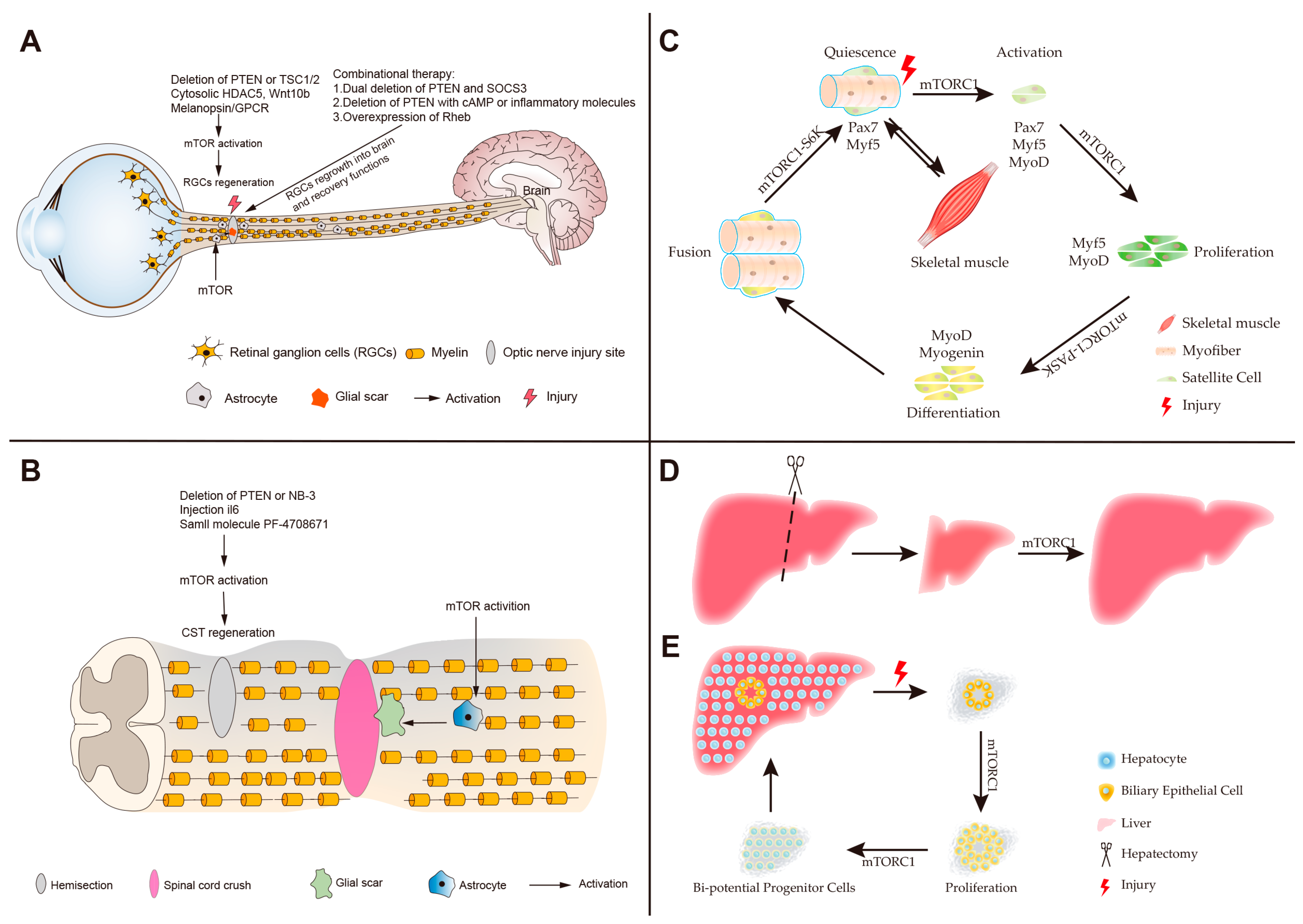
Growth factors, TLR ligands, cytokines, and other extracellular signals can all activate the mTORC1-mTORC2 network in innate immune cells. 216 Studies have demonstrated that mTOR signaling also

mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease Biology Diagrams
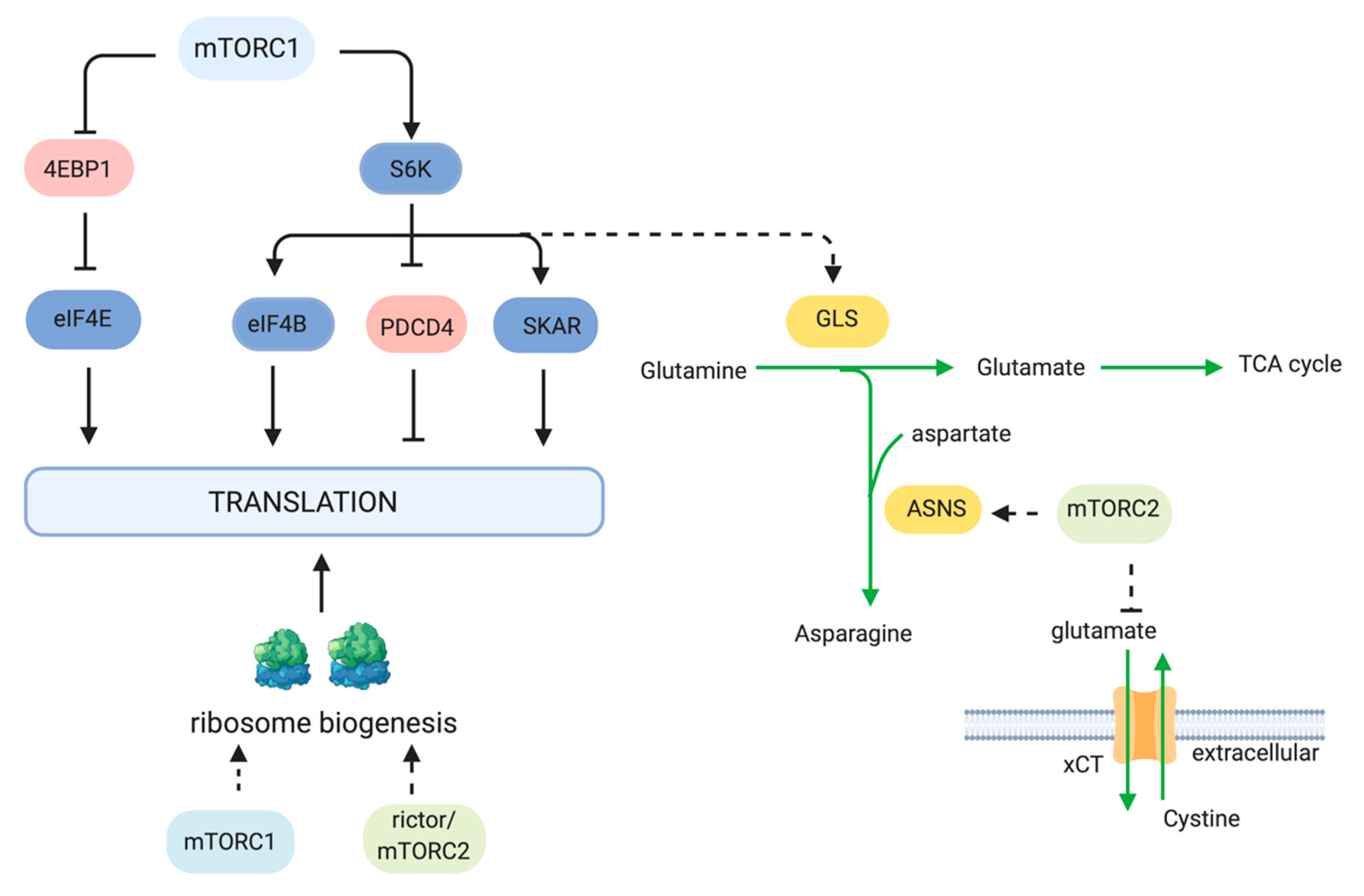
ology. Many aspects of mTOR function and regulation have only recently been elucidated, and many more questions remain un-answered. In this review, we provide an overview of our current understanding of the mTOR pathway and its role in growth, metabolism, and disease. mTORC1 and mTORC2 mTOR is a serine/threonine protein kinase in the PI3K-related The mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) coordinates eukaryotic cell growth and metabolism with environmental inputs including nutrients and growth factors. Extensive research over the past two decades has established a central role for mTOR in The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) coordinates eukaryotic cell growth and metabolism with environmental inputs, including nutrients and growth factors. we provide an overview of our current understanding of the mTOR pathway and its role in growth, metabolism, and disease. mTORC1 and mTORC2. mTOR is a serine/threonine protein kinase