Effects Of Eutrophication On An Ecosystem Biology Diagrams
Effects Of Eutrophication On An Ecosystem Biology Diagrams Eutrophication, the gradual increase in the concentration of phosphorus, nitrogen, and other plant nutrients in an aging aquatic ecosystem such as a lake. Black Sea and elsewhere, hypoxic waters from cultural eutrophication have resulted in massive fish kills, with rippling effects throughout the food chain and local economies. Britannica Quiz. Eutrophication can disrupt the food web in aquatic ecosystems. As algae dominate the system, they may prevent the growth of submerged plants that serve as food for herbivores such as snails and small fish. The reduction in plant life affects the entire food chain, including organisms that rely on these plants for shelter and nutrition. 5. Causes and effects of eutrophication: Eutrophication is characterized by dense algal and plant growth owing to increased concentration of chemical nutrients needed for photosynthesis. In an ecological food chain, consumers are classed into primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers. Primary consumers make up the second trophic level as they
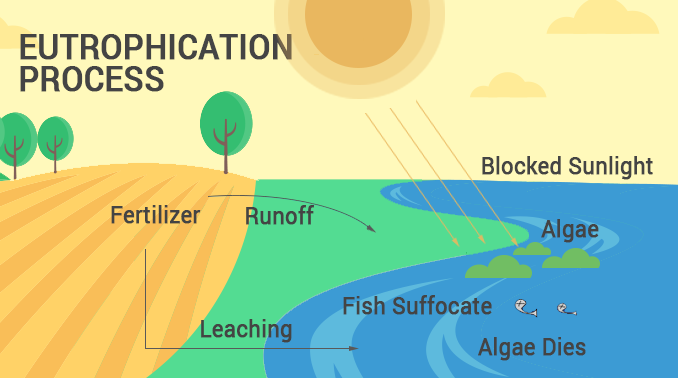
Natural Eutrophication. A process occurring as a lake or river ages hundreds or thousands of years is called natural eutrophication. It happens gradually by addition of nutrients from decaying plants and animals in a water body. This type of eutrophication occurs slowly and results from the natural aging of the water body. Cultural Eutrophication

Eutrophication: Causes, Types, and Effects • Microbe Online Biology Diagrams
Eutrophication, which is caused by nitrate and phosphate runoff from farmlands, effluent from aquaculture ponds as well as municipal and industrial discharge, is a major predicament because of its momentous contributions to the socio-economic and environmental health problems (Carpenter, 2008; Akinnawo, 2021).Moreover, cyanobacterial blooms are amongst the stern consequences of eutrophication

According to a MTT Agrifood Research Finland study, eutrophication affects 57 percent of Finland's domestic food chain contribution to its national economy. Limiting Effects on the Food Chain Limiting water pollutants is crucial because they find their way into our entire food supply, from meats and dairy products, to fruits and vegetables. The widening of the food chain and the diversified basis for the increased productivity influence the ecosystem at large. This was partly counterbalanced by a thinning of the highest trophic levels through human overexploitation of the increased production of dominant fish species, and through the negative consequences on the aquatic ecosystem
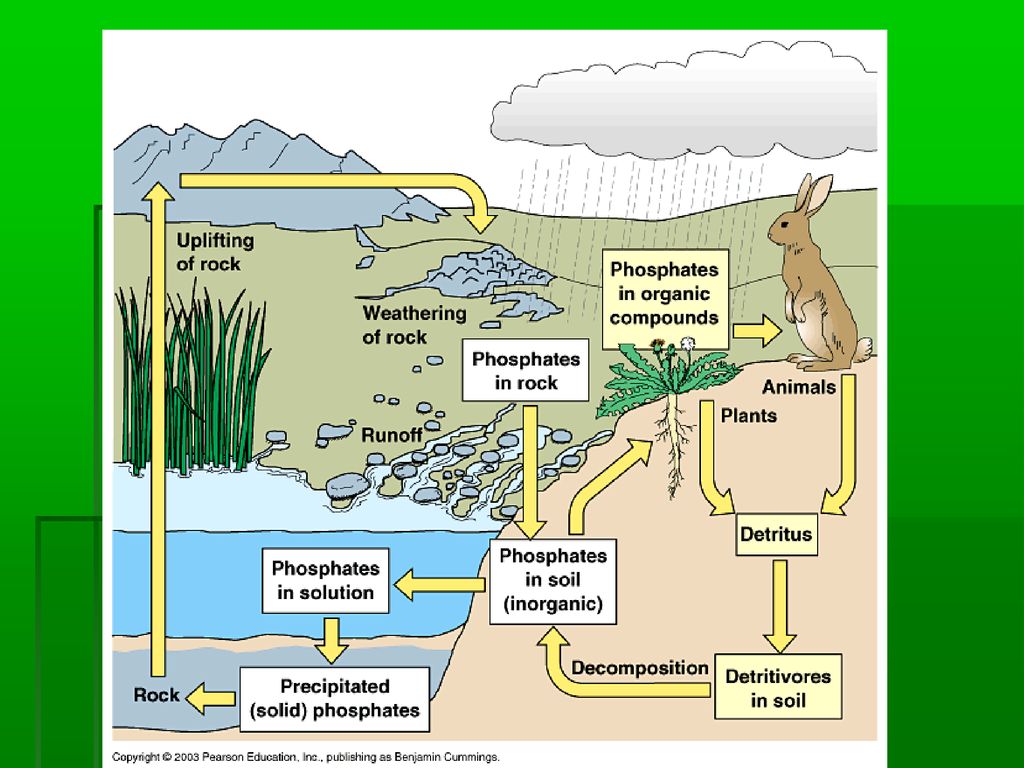
Definition, Causes, Types, Process, Examples Biology Diagrams
78% of global ocean and freshwater eutrophication is caused by agriculture. 1 Eutrophication is the pollution of waterways with nutrient-rich water. supply chains account for 18% of food emissions. This includes food processing, distribution, transport, packaging, and retail. CO 2 eq and warming effects are measured over a 100-year
